CTIA GROUP LTD tungsten alloy rods are alloy materials with tungsten as the matrix and added nickel, iron, copper and other elements. They combine high density, high strength, high temperature resistance, wear resistance and good electrical/thermal conductivity. They are widely used in medical collimators, aerospace counterweights, armor-piercing projectile cores for national defense, electronic electrodes, sports dart shafts and plasma-facing materials for nuclear reactors, serving as key materials in high-end manufacturing. For any tungsten alloy rod products, please contact CTIA GROUP LTD: sales@chinatungsten.com, 0592-5129595.

There are many types of tungsten alloy rods. According to material composition, they can be divided into tungsten-copper alloy rods, tungsten-silver alloy rods, tungsten-nickel-iron alloy rods, etc.; according to size, they can be divided into long alloy rods, short alloy rods, etc.; according to magnetism, they can be divided into magnetic alloy rods and non-magnetic alloy rods; according to shape, they can be divided into cylindrical rods, square rods, conical rods, etc.; according to processing type, they can be divided into sintered rods, swaged rods, forged rods, etc.; according to application, they can be divided into W-Ni-Fe armor-piercing projectile cores for military and defense, W-Cu electrodes for the electronics industry, W-Ni-Fe dart shafts for sporting goods, etc.
1. Tungsten Alloy Rods of Different Compositions
Tungsten alloy rods are mainly classified by composition with tungsten as the matrix. Performance is optimized by adding different metal elements, with tungsten content typically between 90%–97% and the balance being nickel, iron, copper, silver, molybdenum, etc. The common types are as follows:
Tungsten-copper alloy rod (W-Cu): tungsten content 50%–90%, copper 10%–50%, typical grades such as WCu70/30, WCu80/20. The copper phase provides excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, while the tungsten phase provides high hardness and arc ablation resistance. Suitable for electrodes, heat sinks and high-frequency electronic devices.
Tungsten-silver alloy rod (W-Ag): tungsten content 65%–85%, silver 15%–35%. Silver imparts good electrical conductivity and oxidation resistance, while tungsten improves wear resistance and strength. Mainly used for high-voltage electrical contacts, vacuum switches and aerospace relays.

Tungsten-molybdenum alloy rod (W-Mo): tungsten content 70%–90%, molybdenum 10%–30%. Molybdenum solid-solution strengthens the tungsten lattice, increasing recrystallization temperature and high-temperature strength. Suitable for high-temperature furnace heating elements, sputtering targets and aerospace nozzles.
Tungsten-nickel-copper alloy rod (W-Ni-Cu): tungsten content 90%–97%, nickel-to-copper ratio usually 7:3 or 8:2. Tungsten-nickel-copper alloy is non-magnetic, with controllable density and good ductility. Widely used in medical collimators and aerospace counterweights.
Tungsten-nickel-iron alloy rod (W-Ni-Fe): tungsten content 90%–97%, nickel-to-iron ratio 7:3 or 4:1. Iron promotes sintering densification, nickel improves toughness, and the alloy exhibits slight magnetism. Suitable for radiation shielding, automotive counterweights, sporting goods counterweights and vibration damping components.
Tungsten-containing high-entropy alloy rod: composed of five or more principal elements such as tungsten, molybdenum, titanium, etc., in equal or near-equal atomic ratios, with each element accounting for 5%–35% of the total composition. This material exhibits comprehensive advantages far superior to traditional alloys in phase stability, strength-toughness balance, corrosion resistance and radiation damage resistance, usually prepared by vacuum arc melting.

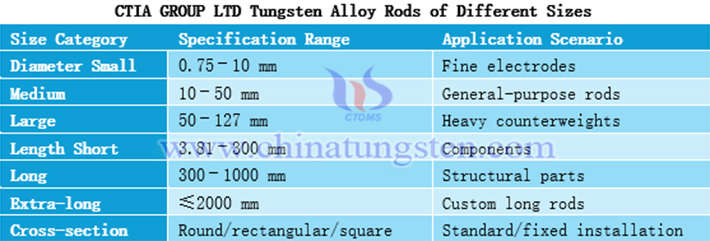
2. Tungsten Alloy Rods of Different Sizes
CTIA GROUP LTD tungsten alloy rods cover sizes from micron to meter scale, with diameters as small as 0.75 mm (electrodes) and as large as 127 mm (counterweights), and lengths customizable up to 2000 mm; cross-sections can be round or rectangular for flexible installation.
3. Tungsten Alloy Rods with Different Magnetic Properties
The magnetism of CTIA GROUP LTD tungsten alloy rods is determined by their constituent metal elements: W-Ni-Fe alloy rods have slight magnetism and lower cost but are prohibited in electromagnetically sensitive areas; W-Ni-Cu alloy rods are non-magnetic and are the preferred materials for medical and avionics fields.

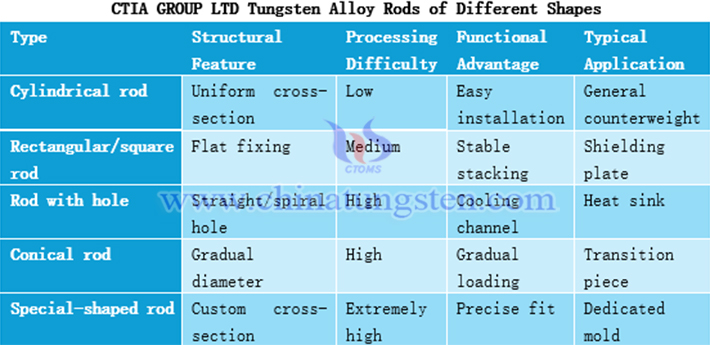
4. Tungsten Alloy Rods of Different Shapes
The shapes of CTIA GROUP LTD tungsten alloy rods can extend from standard cylinders to complex special shapes to meet various installation and functional requirements. Among them, cylindrical and rectangular tungsten alloy rods are easy to process and highly versatile; rods with holes and conical rods can support cooling functions and gradual load scenarios; special-shaped rods enable high-precision customization.
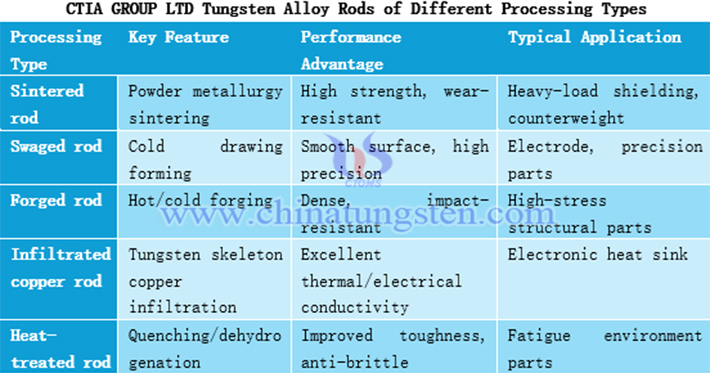
5. Tungsten Alloy Rods of Different Processing Types
Processing type affects the surface quality, dimensional accuracy and mechanical strength of tungsten alloy rods. Among them, sintered rods have high strength and good wear resistance, suitable for shielding scenarios; swaged rods have smooth surfaces and high precision, making them the preferred material for electrodes; forged rods have dense structure and strong impact resistance, suitable for structural parts; infiltrated copper rods have excellent thermal conductivity for thermal management; heat-treated rods have high toughness and good fatigue resistance.
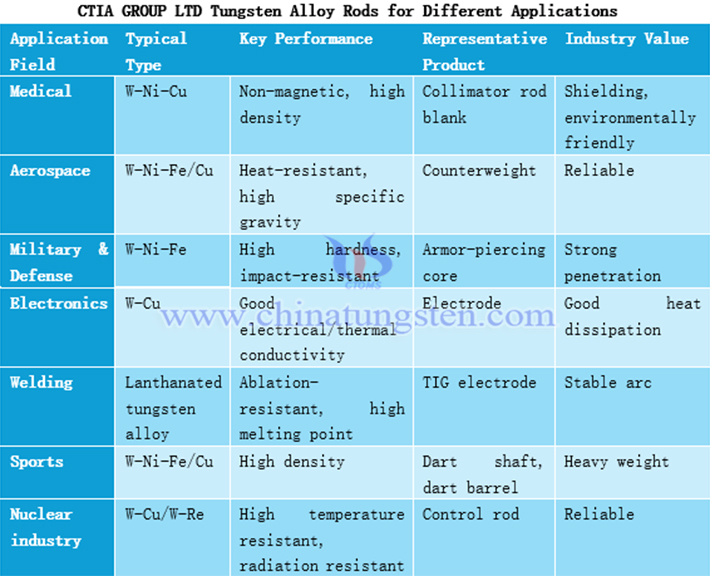
6. Tungsten Alloy Rods for Different Applications
Depending on the application, tungsten alloy rods can be divided into W-Ni-Fe/Cu counterweights for aerospace, W-Ni-Fe armor-piercing projectile cores for military and defense, W-Cu electrodes for the electronics industry, W-Ni-Fe dart shafts for sporting goods, etc.
?



